When your Windows PC flashes that all-too-familiar “No Internet” message—especially while using an Ethernet cable—it can feel unnecessarily frustrating. Ethernet is supposed to be the stable one, right? It’s often more reliable than Wi-Fi, so seeing it fail leaves you wondering where things went sideways.
The cause might be surprisingly simple, like a loose connection, or it might dig deeper—perhaps a misbehaving driver or some obscure network configuration issue. Either way, you don’t need to panic. This step-by-step guide will walk you through the most effective ways to troubleshoot and fix Ethernet-related “No Internet” errors on a Windows PC.
How to Fix “No Internet” in Windows When Using Ethernet
A “No Internet” message with an Ethernet setup usually signals that something along the chain—from your PC to your router/modem, and out to your ISP—is broken. Often, it’s something minor. So let’s start with the basics and work our way toward more advanced fixes.
Step 1: Begin with the Obvious (and Most Overlooked) Checks
Inspect the Ethernet Cable
It sounds obvious, but you’d be surprised how often the cable itself is the culprit.
- Make sure it’s snugly connected on both ends—PC and router.
- Look for LED lights near the Ethernet port. No lights? That’s usually a red flag.
- If you have another cable handy, give it a try. Sometimes cables go bad.
- Also, double-check you’re using an actual Ethernet cable (Cat5e or Cat6), not a lookalike phone cord.
Restart Your Modem and Router
Sometimes, your equipment just needs a fresh start.
- Unplug both modem and router.
- Wait about 30–60 seconds.
- Plug in the modem first, let it stabilize.
- Then plug in the router.
- Restart your PC.
Check Indicator Lights
On both modem and router:
- A steady “Internet” or “WAN” light is a good sign.
- Blinking erratically, off, or red? You might be looking at an ISP issue. Consider calling them.
Try Another Device
Can other devices connect to the internet using the same router?
- If yes, the issue is likely your Windows PC.
- If no, the problem is more likely with your modem/router or the ISP.
Step 2: Check Windows Settings and Tools
Run the Network Troubleshooter
Sometimes, Windows can diagnose itself.
- Windows 11: Settings > Network & internet > Advanced network settings > Network troubleshooter.
- Windows 10: Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network troubleshooter.
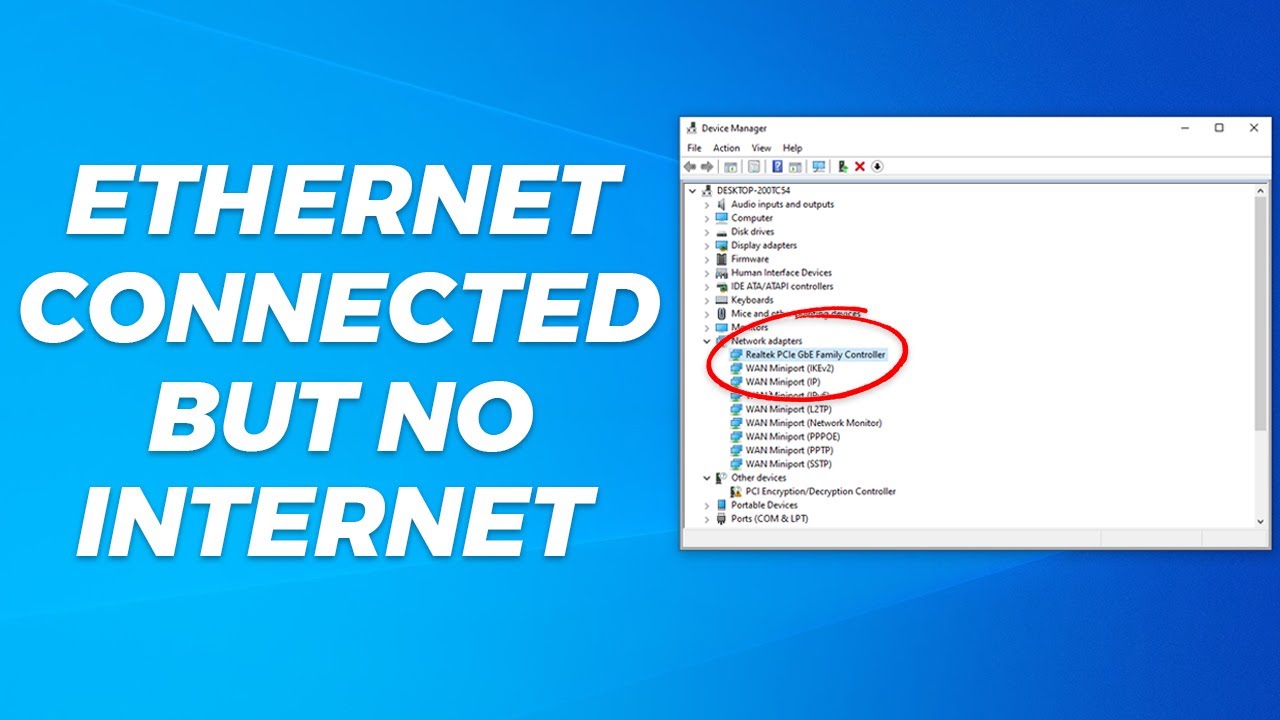
Look at Your Ethernet Adapter
- Right-click Start > Device Manager > Network adapters.
- Look for any warning signs (like a yellow exclamation point or red X).
- If it’s disabled (you’ll see a down arrow), right-click and choose “Enable.”
Update or Reinstall Drivers
- In Device Manager, right-click the Ethernet adapter.
- Try “Update driver” > “Search automatically.”
- If that fails, visit your PC/motherboard manufacturer’s site for the latest driver.
- As a last resort, uninstall the device and restart your PC. Windows should reinstall a default driver.
Reset Network Adapters
A full reset can often wipe out hidden issues.
- Windows 11: Settings > Network & internet > Advanced network settings > Network reset.
- Windows 10: Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network reset.
- Click “Reset now” and reboot your PC.
Step 3: Dive Into Network Configuration
Refresh Your IP
Sometimes your PC clings to an expired IP address.
- Open Command Prompt (Admin).
- Type: ipconfig /release
- Then: ipconfig /renew
- To verify: ipconfig /all
Flush DNS Cache
A corrupt DNS cache can stall browsing.
- In the same Command Prompt:
- ipconfig /flushdns
- netsh int ip reset
- netsh winsock reset
- Restart your PC.
Double-Check Proxy Settings
- Windows 11: Settings > Network & internet > Proxy.
- Windows 10: Settings > Network & Internet > Proxy.
- Ensure “Automatically detect settings” is ON.
- Make sure manual or script settings are OFF—unless you specifically use a proxy.
Disable Security Software Temporarily
Firewalls and antivirus programs sometimes block legit traffic.
- Try disabling Windows Firewall or third-party antivirus software briefly.
- If this restores your connection, look into creating an exception rather than leaving it off.
Step 4: Advanced Troubleshooting
Check for IP Conflicts
If two devices fight over the same IP, it can get messy.
- Log into your router (typically at 192.168.1.1 or 192.168.0.1).
- Look for duplicate IPs in the DHCP client list.
- Restart the affected devices or set a static IP.
Investigate VPN Software
Some VPNs can mess with network access even when they’re turned off.
- Try uninstalling it completely and see if that resolves things.
Scan for Malware
Malware can disrupt connections in all sorts of sneaky ways.
- Run a full system scan using Windows Defender or a trusted third-party antivirus.
Try a Clean Boot
To rule out software conflicts:
- Perform a clean boot (search Microsoft’s guide on how to do this).
- If the internet works, re-enable startup programs one by one to find the issue.
Reinstall Windows (Only If You Must)
If nothing else works:
- Backup your data.
- Perform a clean install of Windows. This is the nuclear option—but it can fix deeply-rooted issues.
Final Thoughts
Dealing with a “No Internet” message on an Ethernet connection might feel overwhelming at first, but it’s rarely unsolvable. By methodically checking each layer—from physical cables and router restarts to Windows settings and driver configurations—you can often get things back up and running without needing to call in a tech pro.